
In this blog, we are going discuss some additional features in Google Workspace and Google Vault.
Admins in Google Workspace can allow users in the organization to do all Vault tasks or only a specific subset. For example, they might allow certain users to set retention rules, and allow a different group to search and export data. Consultation with the organization’s legal experts is recommended before giving users Vault privileges and determine which users require access to Vault tools. Accounts with Vault privileges should be treated as sensitive because they have access and control over other users’ data in your organization. Admins can give a user Vault privileges without giving them a Vault license. Users don’t need Vault licenses to have Vault privileges.
Vault privileges are categorized as below, you can restrict the scope of the role to a specific organizational unit with these categorized privileges: Search and export-related privileges, Holds, audits, and matter-related privileges, Retention-related privileges:
- Manage Exports
- Manage Searches,
- Manage Holds
- Manage Matters
- Manage Audits
- Manage Retention Policies
- View Retention Policies
View All Matters
It is important to know the limitations and scope of the privileges for an organizational unit, super administrators, or other users outside the organizational unit. For example:
- Google Workspace super administrators don’t have access to all exports. They can only work with exports they own and exports in matters shared with them.
- When Manage Holds is restricted to an organizational unit, the user can create and remove holds only for accounts in the organizational unit. Vault users outside the organizational unit can see holds on users in the organizational unit.
- The user won’t see any matters if they don’t own any and don’t have any shared with them. If the user’s admin role doesn’t include the View All Matters privilege, then the user can only see matters they own, and matters shared with them.
- One of the interesting features in Google Vault is grant access and assign privileges to an external user. Your organization can grant Vault access to external users, such as the members of a regulatory agency, to comply with an investigation or audit.
- You need to consider if you delete a user, all the data for that user is removed from Google and you can`t search for any of the deleted user`s data from Vault and any retention rules or holds no longer apply. Data can be recovered for 20 days after user deletion. But any data that is already expunged can’t be recovered. Google recommends use an Archived User (AU) license to preserve the user’s data. But in Google Cloud Directory Sync, there is an option that you can configure the tool to suspend accounts instead of deleting them.
- Across all of Vault or in a specific matter, you can review the activity of Vault users in Vault. For example, audit all of Vault to learn which Vault users edited retention rules. Or audit a specific matter to learn who downloaded export files from that matter.
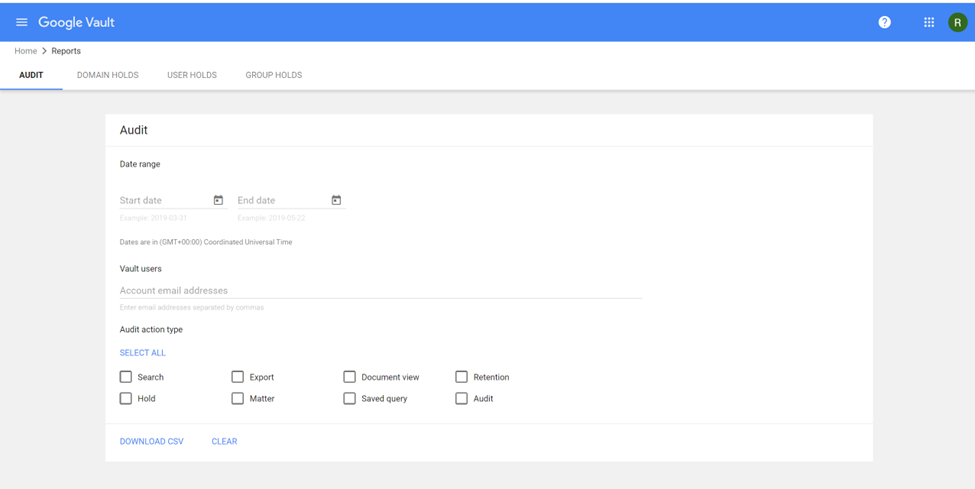
Audit activity across all off Vault
- Sign in to vault.google.com.
- Click Reports.
- Select a date range (Optional).
- Enter the email addresses of the Vault users whose actions you want to audit (Optional). To audit the actions of all Vault users, leave the field empty.
- Select what types of Vault user actions you want to audit:
- To audit all actions, click Select All.
- To audit only some actions, check the box next to each action.
- Click Download CSV. A CSV file that contains audit information is downloaded to your device.
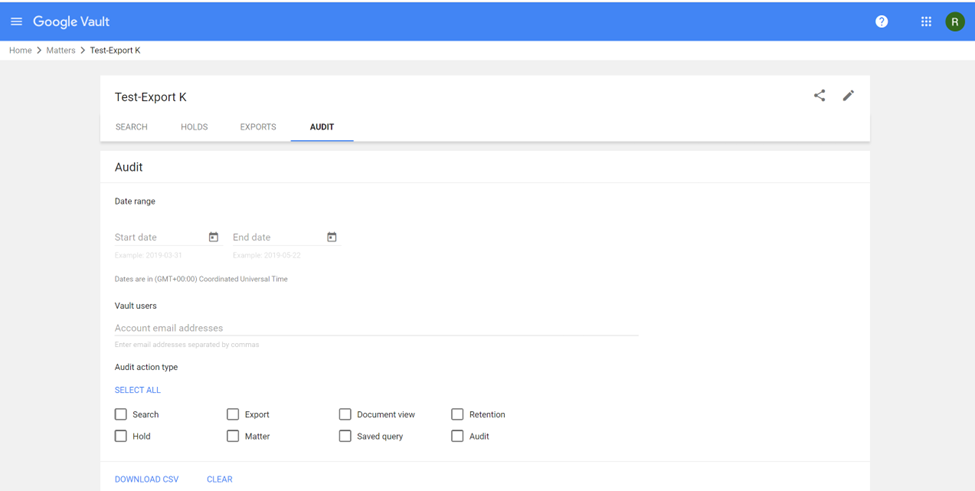
Audit activity in a specific matter
- Sign in to vault.google.com.
- Click Matters.
- In the list of matters, click the matter you want to audit.
- Click Audit.
- Select a date range (Optional).
- (Optional) Enter the email addresses of the Vault users whose actions you want to audit. To audit the actions of all Vault users, leave the field empty.
- Select what types of Vault user actions you want to audit:
- Click Download CSV. A CSV file that contains audit information is downloaded to your device.
In Google Admin Center, by adding an account to a specific organizational unit (to control access by department) or to an access group (to allow access for users across or within departments), admins can:
- Turn on a service.
- Set up auto replies for a group.
- Set the group email language.
- Add a footer to a group’s email.
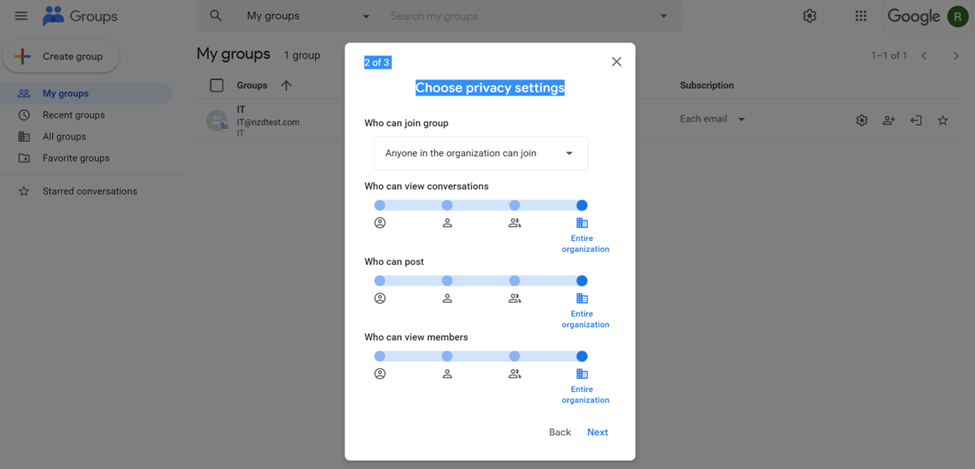
- Choose who can see your groups, who can join the group.
- Lock a conversation.
- Set the service to be Inherited form its parent or be overridden.
- Make a group a Collaborative Inbox
When you create a group, you see some default configuration and you see some boxes to change the privileges, an owner or manager can assign each permission to different sets of users:
- The default group roles (owners, managers, or members)
- Everyone in the organization
- Everyone on the web
- Specially created custom roles
Would you like to learn more about our services? Email [email protected] or call 289-803-9730. We would be happy to share more details about our self-service or fully managed eDiscovery services!





